Very High
Windows Remote Desktop (RDP) Use-after-free vulnerablility, "Bluekeep"
CVE ID
AttackerKB requires a CVE ID in order to pull vulnerability data and references from the CVE list and the National Vulnerability Database. If available, please supply below:
Add References:
Windows Remote Desktop (RDP) Use-after-free vulnerablility, "Bluekeep"
MITRE ATT&CK
Collection
Command and Control
Credential Access
Defense Evasion
Discovery
Execution
Exfiltration
Impact
Initial Access
Lateral Movement
Persistence
Privilege Escalation
Topic Tags
Description
A bug in Windows Remote Desktop protocol allows unauthenticated users to run arbitrary code via a specially crafted request to the service. This affects Windows 7/Windows Server 2008 and earlier releases. Given the ubiquity of RDP in corporate environments and the trusted nature of RDP, this could pose serious concerns for ransomware attacks much like WannaCry.
Patches are released for Windows 7/2008 Operating systems as well as Windows XP.
Add Assessment
Ratings
-
Attacker ValueVery High
-
ExploitabilityMedium
Technical Analysis
The effort to execute the exploit out of the box, with default settings on known targets is not that high. It’s important to note that to exploit this reliably in atypical scenarios you need to know a bit more detail of the target, including what hypervisor it may be running on.
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportRatings
-
Attacker ValueHigh
-
ExploitabilityLow
Technical Analysis
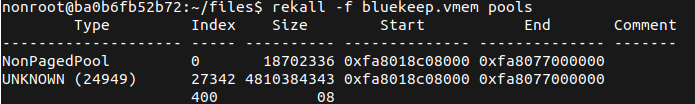
Like some others have said, this requires an understanding of your targets Host devices in order to generate a reliable exploit. This involves identifying the Start address of the NonPageedPool and plugging this into the existing metasploit module.
With a large number of cloud-based resources this is perhaps a little easier to exploit than enterprise desktops.
An example against AWS hosted windows appliances works something like this.
- Spin up your own AWS Instance.
- Use Memory Dump tool like WinPMem to grab a memory image.
- Transfer mem dump to a machine running the rekall memory forensics tool
- Run the
poolsplugin to get the address.
This offset will work against any instance in this region started from that same base AMI.
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportRatings
-
Attacker ValueHigh
-
ExploitabilityHigh
Technical Analysis
What a pain to make it work generally across different versions! The work put into this will be foundational for future exploit development around RDP and Windows kernel exploitation in general.
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportRatings
-
Attacker ValueVery High
-
ExploitabilityVery Low
Technical Analysis
It is a scary vuln, and you should patch immediately. As no PoC is out, don’t trust the patch entirely and limit exposure to critical systems.
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportRatings
-
Attacker ValueVery High
-
ExploitabilityVery Low
Technical Analysis
This vuln is important to focus attention to. Pre-auth RCE on a likely large target base is very dangerous.
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportRatings
-
Attacker ValueLow
-
ExploitabilityVery Low
Technical Analysis
This vulnerability may seem very useful, it is probably as interesting as other RCEs affecting Microsoft Windows OSes, however public exploits rely on the existence of a registry key (fDisableCam) not being present by default (it has to be manually created) thus not found in enterprise networks.
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportRatings
-
Attacker ValueVery High
-
ExploitabilityVery Low
Technical Analysis
Watch this one for details. In the meantime, if you can’t patch, then block TCP/3389 (or whatever port you might be mapping RDP to), enable Network Level Authentication (NLA), or disable RDP.
This exploit is critical. RDP is ubiquitous in corporate settings, which are the most likely to have older Operating Systems deployed. That issue is complicated by the general reasoning that most older Operating systems are there to support legacy equipment and are less likely to receive automated patching.
EDIT (24-July-2019): Welp, we’ve heard lots of researchers say they’re privately holding onto PoCs, but now PoCs and details are starting to surface. It won’t be long until this one is easily weaponized, and I’m willing to bet it’s being used in the wild, if only in selected cases.
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportRatings
-
Attacker ValueVery High
-
ExploitabilityMedium
Technical Analysis
Description
A vulnerability in the RDP windows service allows the execution of malicious code with the injection of code in the request for a RDP connection. The exploitation of this vulnerability may be used for performing a DoS (Denial Of Service) attack or executing code in a remote system.
For the safe and satisfactory exploitation of this vulnerability, it is recommended to identify the target machine so the exploit is reliably crafted.
Mitigation
- Apply the corresponding security patches released by Microsoft (supported and unsupported OSs)
- Disabling RDP service where no needed and controlling its exposure using a FW internally and externally
- Enabling network level authentication in RDP services
Affected Systems
The following Operating System are affected if they have not been patched:
- Windows Vista
- Windows 7
- Windows XP
- Windows Server 2003
- Windows Server 2008
References
- The exploit is now included in Metasploit. (The exploit may requier some tuning)
- https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2019-0708
Personal Notes
When I have released this assessment, the coronavirus crisis has required for a massive number of companies and entities to go “remote work”, and an important increment in exposed RDP services on the internet has been detected. Need to emphasize ICS environments and the infrastructure supporting heath services.
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportCan you help me to use that? I’m teaching the IA to auto-exploit :D
Ratings
Technical Analysis
Some of the gotchas on patching this vuln:
- Not restarting the vulnerable asset, even after you apply the patch, keeps the asset vulnerable. Must restart.
- There have been cases where even with the patch reported as being installed, files on disk were vulnerable, manually checking termdd.sys, the file is normally located at C:\Windows\System32\drivers and the version retrieved with this powershell command:
get-item -Path ‘C:\Windows\System32\drivers\termdd.sys’ | Format-List -Force
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportRatings
-
Attacker ValueVery High
-
ExploitabilityMedium
Technical Analysis
Due to public exploits being flaky and sometimes resulting in a Blue Screen on the victim, this exploit is still somewhat difficult to always replicate. If you have paid tools that have better versions of the exploit, it’s more reliable.
The fact that an exploit is included in newer versions of metasploit massively lowers the bar for being able to exploit this vulnerability.
The damage potential is astronomical as there are so many machines that expose RDP to the internet.
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportRatings
-
Attacker ValueVery High
-
ExploitabilityMedium
Technical Analysis
What Aaron said. I was neutral on ratings I don’t have enough information on.
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportThis removes the syscall hooking in the BlueKeep exploit, adapting it for targets with the Meltdown patch installed: https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-framework/pull/12553. The result is improved exploit reliability for those targets.
Technical Analysis
CVE-2019-0708 has supposively been exploited in the wild by Chinese state actors according to the NSA announcement at https://media.defense.gov/2020/Oct/20/2002519884/-1/-1/0/CSA_CHINESE_EXPLOIT_VULNERABILITIES_UOO179811.PDF
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportRatings
Technical Analysis
Exploited by North Korean state-sponsored attackers according to a July 2024 bulletin from multiple U.S. government agencies: https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/cybersecurity-advisories/aa24-207a
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportCVSS V3 Severity and Metrics
General Information
Vendors
Products
Exploited in the Wild
- Government or Industry Alert (https://www.ic3.gov/Media/News/2022/220126.pdf)
- News Article or Blog (https://www.ibm.com/downloads/cas/M1X3B7QG)
- Other: Ransomware Report 2023 (https://cybersecurityworks.com/howdymanage/uploads/file/Ransomware%20Report%202023_compressed.pdf)
Would you like to delete this Exploited in the Wild Report?
Yes, delete this reportWould you like to delete this Exploited in the Wild Report?
Yes, delete this reportReferences
Advisory
Miscellaneous
Additional Info
Technical Analysis
Report as Emergent Threat Response
Report as Zero-day Exploit
Report as Exploited in the Wild
CVE ID
AttackerKB requires a CVE ID in order to pull vulnerability data and references from the CVE list and the National Vulnerability Database. If available, please supply below: