bulw4rk (18)
Last Login: October 02, 2020
bulw4rk's Latest (3) Contributions
Technical Analysis
Description
A vulnerability in the RDP windows service allows the execution of malicious code with the injection of code in the request for a RDP connection. The exploitation of this vulnerability may be used for performing a DoS (Denial Of Service) attack or executing code in a remote system.
For the safe and satisfactory exploitation of this vulnerability, it is recommended to identify the target machine so the exploit is reliably crafted.
Mitigation
- Apply the corresponding security patches released by Microsoft (supported and unsupported OSs)
- Disabling RDP service where no needed and controlling its exposure using a FW internally and externally
- Enabling network level authentication in RDP services
Affected Systems
The following Operating System are affected if they have not been patched:
- Windows Vista
- Windows 7
- Windows XP
- Windows Server 2003
- Windows Server 2008
References
- The exploit is now included in Metasploit. (The exploit may requier some tuning)
- https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2019-0708
Personal Notes
When I have released this assessment, the coronavirus crisis has required for a massive number of companies and entities to go “remote work”, and an important increment in exposed RDP services on the internet has been detected. Need to emphasize ICS environments and the infrastructure supporting heath services.
Technical Analysis
Description
The installation of a vulnerable version of Keybase deploys a SUID binary named “keybase-redirector” which calls the “fusermount” binary using a relative path, making the application trust the value of $PATH. This triggers a PATH injection vulnerability which allows local privilege escalation by using a malicious file with its name set to “fusermount”.
Mitigation
The maintainer has released some fixes, so the software must be upgrade to Keybase version 2.8.0-20181023124437 or above.
Affected Systems
All Keybase versions prior to 2.8.0-20181023124437.
PoC
1- We can identify a potential vulnerable installation with the following command, which will help us identify the SUID binary related to Keybase.
find / -perm 4000 2>/dev/null | grep keybase
2- To verify the vulnerability, we check the output of the following command is prior to 2.8.0-20181023124437.
keybase -v
3- In case the the software version is vulnerable, we may create a malicious binary (which executes, for example, a rshell, creates a high privilege user, etc.) with the name fusermount and deploy it on a directory to be injected on the PATH.
NOTE: Development and compilation of the binary left for the tester
4- We add the directory in the first position inside the path variable and execute the Keybase software.
env PATH=<malicious_dir_path>:$PATH /usr/bin/keybase-redirector /keybase
This will execute the payload inside the malicious binary as root.
Personal Notes
In some engagements, I have seen this software installed on workstation or servers from DevOps/SecDevOps teams, where they manage access keys and credentials for critical corporate infrastructure. Because of this, a Keybase vulnerable installation should not be taken lightly.
Technical Analysis
Description
Due to a pre-authenticated Path Trasversal vulnerability under the SSL VPN portal on FortiOS, an attacker is able to pull arbitrary system files from the file system. One of the most critical files which an attacker may pull is “sslvpn_websessions” which contains session information including usernames and password.
Once the attacker has obtained the credentials from this file, he can authenticated with those credentials, compromising the corporate perimeter.
Mitigation
- Upgrade to FortiOS 5.4.13, 5.6.8, 6.0.5 or 6.2.0 and above.
- Enable 2FA. Note the attacker will not be able to log in to the VPN, but the obtained credentials are still valid (potencial domain creds) to access corporate mail, etc.
Affected Systems
- FortiOS 6.0: 6.0.0 to 6.0.4
- FortiOS 5.6: 5.6.3 to 5.6.7
- FortiOS 5.4: 5.4.6 to 5.4.12
NOTE: Only if the SSL VPN service (web-mode or tunnel-mode) is enabled.
PoC
There are some public working exploits for this vulnerability, targeting the “sslvpn_websessions” system file.
An attacker would access the following URL:
- https://
<IP_ADDRESS>/remote/fgt_lang?lang=/../../../..//////////dev/cmdb/sslvpn_websession
And after some parsing to the binary file, something like the following output would be obtained:
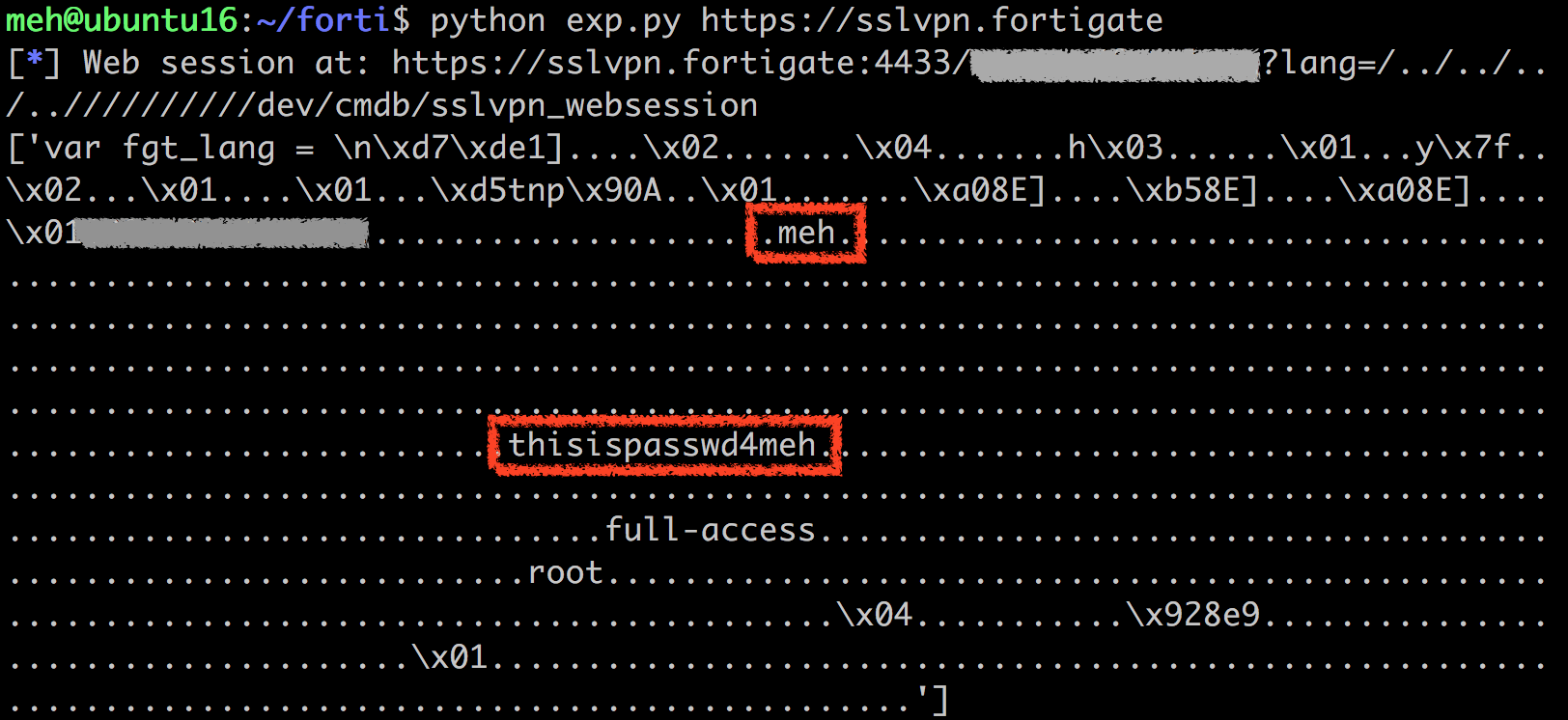
NOTE: Example image obtained from https://devco.re/blog/2019/08/09/attacking-ssl-vpn-part-2-breaking-the-Fortigate-ssl-vpn/