Very High
CVE-2018-13379 Path Traversal in Fortinet FortiOS
CVE ID
AttackerKB requires a CVE ID in order to pull vulnerability data and references from the CVE list and the National Vulnerability Database. If available, please supply below:
Add References:
CVE-2018-13379 Path Traversal in Fortinet FortiOS
MITRE ATT&CK
Collection
Command and Control
Credential Access
Defense Evasion
Discovery
Execution
Exfiltration
Impact
Initial Access
Lateral Movement
Persistence
Privilege Escalation
Topic Tags
Description
An Improper Limitation of a Pathname to a Restricted Directory (“Path Traversal”) in Fortinet FortiOS 6.0.0 to 6.0.4, 5.6.3 to 5.6.7 and 5.4.6 to 5.4.12 and FortiProxy 2.0.0, 1.2.0 to 1.2.8, 1.1.0 to 1.1.6, 1.0.0 to 1.0.7 under SSL VPN web portal allows an unauthenticated attacker to download system files via special crafted HTTP resource requests.
Add Assessment
Ratings
-
Attacker ValueVery High
-
ExploitabilityVery High
Technical Analysis
Description
Due to a pre-authenticated Path Trasversal vulnerability under the SSL VPN portal on FortiOS, an attacker is able to pull arbitrary system files from the file system. One of the most critical files which an attacker may pull is “sslvpn_websessions” which contains session information including usernames and password.
Once the attacker has obtained the credentials from this file, he can authenticated with those credentials, compromising the corporate perimeter.
Mitigation
- Upgrade to FortiOS 5.4.13, 5.6.8, 6.0.5 or 6.2.0 and above.
- Enable 2FA. Note the attacker will not be able to log in to the VPN, but the obtained credentials are still valid (potencial domain creds) to access corporate mail, etc.
Affected Systems
- FortiOS 6.0: 6.0.0 to 6.0.4
- FortiOS 5.6: 5.6.3 to 5.6.7
- FortiOS 5.4: 5.4.6 to 5.4.12
NOTE: Only if the SSL VPN service (web-mode or tunnel-mode) is enabled.
PoC
There are some public working exploits for this vulnerability, targeting the “sslvpn_websessions” system file.
An attacker would access the following URL:
- https://
<IP_ADDRESS>/remote/fgt_lang?lang=/../../../..//////////dev/cmdb/sslvpn_websession
And after some parsing to the binary file, something like the following output would be obtained:
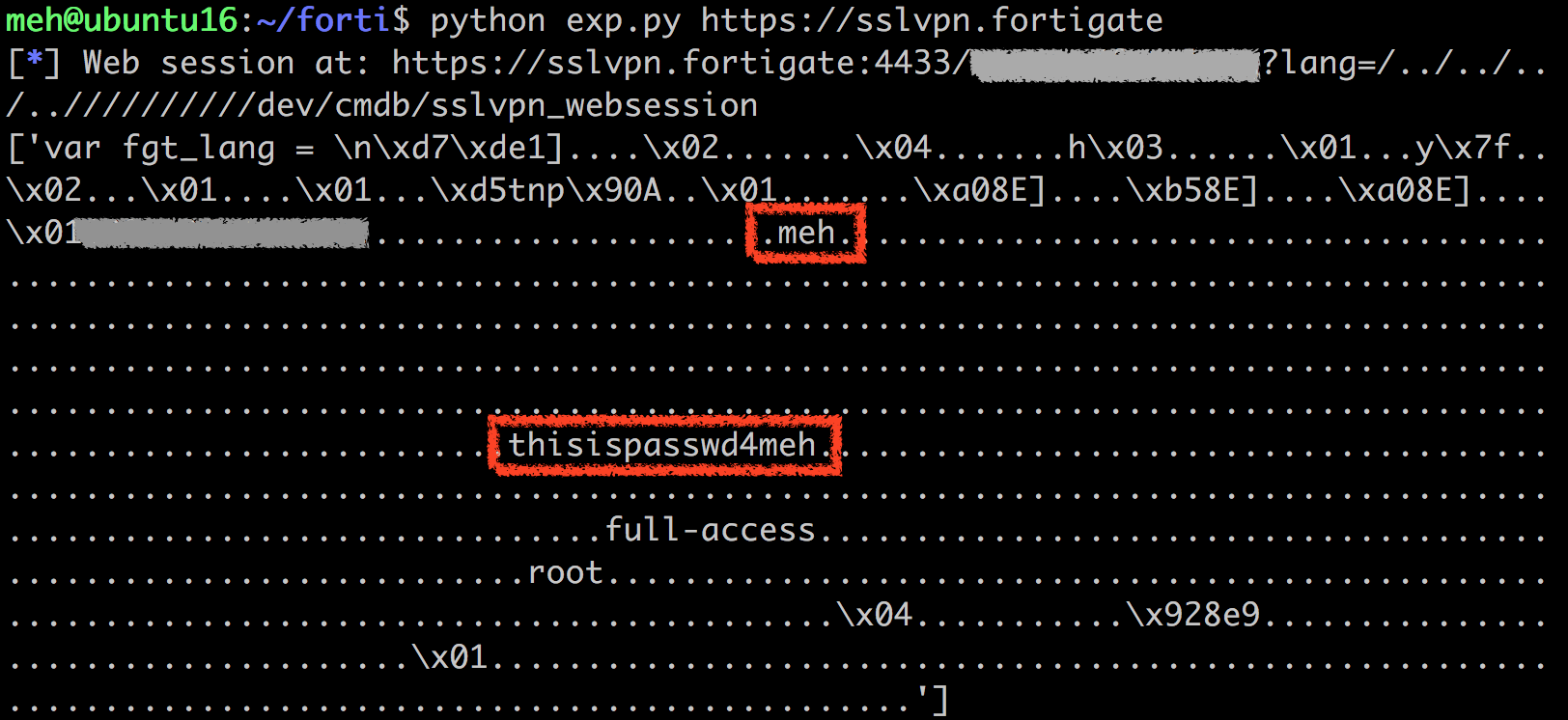
NOTE: Example image obtained from https://devco.re/blog/2019/08/09/attacking-ssl-vpn-part-2-breaking-the-Fortigate-ssl-vpn/
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportTechnical Analysis
Reported as exploited in the wild at https://us-cert.cisa.gov/ncas/alerts/aa20-296a
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportRatings
-
Attacker ValueVery High
-
ExploitabilityHigh
Technical Analysis
Exploit code for VPN credential-stealing is readily available, as is information on unpatched targets. The vuln is known to be exploited by nation state-sponsored threat actors as well as run-of-the-mill attackers. Fortinet customers who discover vulnerable FortiOS VPN devices on their networks will want to conduct incident response investigations in addition to patching.
Would you also like to delete your Exploited in the Wild Report?
Delete Assessment Only Delete Assessment and Exploited in the Wild ReportCVSS V3 Severity and Metrics
General Information
Exploited in the Wild
- Government or Industry Alert (https://us-cert.cisa.gov/ncas/current-activity/2021/04/02/fbi-cisa-joint-advisory-exploitation-fortinet-fortios)
- News Article or Blog (https://www.tenable.com/blog/contileaks-chats-reveal-over-30-vulnerabilities-used-by-conti-ransomware-affiliates)
- Other: Government Advisory (https://www.ic3.gov/Media/News/2021/210527.pdf)
Would you like to delete this Exploited in the Wild Report?
Yes, delete this reportWould you like to delete this Exploited in the Wild Report?
Yes, delete this reportWould you like to delete this Exploited in the Wild Report?
Yes, delete this reportReferences
Miscellaneous
Additional Info
Technical Analysis
Threat status: Widespread threat
Attacker utility: Network pivot / information disclosure
CVE-2018-13379 is a pre-authentication information disclosure vulnerability that arises from a path traversal flaw in the web portal component of FortiOS SSL VPNs, first detailed by prominent security researchers Orange Tsai and Meh Chang in August of 2019. The vulnerability allows external attackers to download FortiOS system files through specially crafted HTTP resource requests. Fortinet has a 2019 blog post on this and other CVEs here; the company also published an additional blog in November 2020 based on ongoing exploitation of the vulnerability. CVE-2018-13379 carries a CVSSv3 base score of 9.8.
CVE-2018-13379 can be used to steal valid session information from vulnerable Fortinet devices and has been broadly and actively exploited in the wild since 2019. Exploitation has continued through 2020 and the beginning of 2021—in November 2020, news articles announced that credentials for roughly 50,000 vulnerable Fortinet VPNs had been leaked, along with other high-value information such as access levels. On April 2, 2021, CISA and the FBI issued a joint alert on exploitation of FortiOS devices by APT groups. CVE-2018-13379, CVE-2019-5591, and CVE-2020-12812 were specified in the warning.
Affected products
FortiOS 6.0 – 6.0.0 to 6.0.4
FortiOS 5.6 – 5.6.3 to 5.6.7
FortiOS 5.4 – 5.4.6 to 5.4.12
(other branches and versions than above are not impacted)
ONLY if the SSL VPN service (web-mode or tunnel-mode) is enabled.
Technical analysis
We have continued to see network access commoditized by both advanced and run-of-the-mill attackers leveraging this and other vulnerabilities; sustained attacks on vulnerable Fortinet devices—whether targeting this vulnerability or others—have indicated that many organizations’ patch cycles are significantly behind attacker capabilities. See existing technical assessments by AttackerKB users for additional specific analysis of this vulnerability.
Guidance
The original guidance for this vulnerability (from 2019) advised Fortigate customers to upgrade their FortiOS devices to 5.4.13, 5.6.8, 6.0.5 or 6.2.0 and above, depending on which firmware version stream those customers’ devices were using. As nearly two years have passed since Fortinet issued the original updates in May of 2019, however, we strongly advise that FortiOS customers upgrade to the latest version supported by their devices as soon as possible, without waiting for normal patch cycles: https://docs.fortinet.com/product/fortigate/7.0
If you have been running a vulnerable version of FortiOS, we also recommend conducting an investigation into whether your device(s) and networks may have been compromised. Given the criticality of these devices, organizations would be well-advised to adhere to as small a patch window as possible, and to implement a “zero-day” patch cycle if possible.
References
https://blog.orange.tw/2019/08/attacking-ssl-vpn-part-2-breaking-the-fortigate-ssl-vpn.html
https://www.fortinet.com/blog/psirt-blogs/fortios-ssl-vulnerability
https://www.fortiguard.com/psirt/FG-IR-18-384
https://docs.fortinet.com/product/fortigate/7.0
https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/passwords-exposed-for-almost-50-000-vulnerable-fortinet-vpns/
https://us-cert.cisa.gov/ncas/current-activity/2019/10/04/vulnerabilities-exploited-multiple-vpn-applications
https://us-cert.cisa.gov/ncas/current-activity/2021/04/02/fbi-cisa-joint-advisory-exploitation-fortinet-fortios
Report as Emergent Threat Response
Report as Zero-day Exploit
Report as Exploited in the Wild
CVE ID
AttackerKB requires a CVE ID in order to pull vulnerability data and references from the CVE list and the National Vulnerability Database. If available, please supply below:





Here is the first repo I found on a DDG search.
https://github.com/milo2012/CVE-2018-13379/blob/master/CVE-2018-13379.py
Neat, this sounds important to patch!